Overview
This article aims to help you understand the normal range for the estimated Average Glucose (eAG) test, which is vital for effective diabetes management.
Are you feeling overwhelmed by the complexities of diabetes? You’re not alone.
Maintaining eAG levels between 70 mg/dL and 126 mg/dL is essential for minimizing health risks associated with diabetes.
Research shows that regular monitoring and making lifestyle changes can significantly improve your health outcomes and reduce complications.
Remember, we’re here for you on this journey. Together, we can achieve your goals and enhance your well-being.
Introduction
Understanding blood sugar management can feel overwhelming, especially for those navigating the complexities of diabetes. The estimated Average Glucose (eAG) test is a vital tool that can help. It translates A1C results into a more understandable format, reflecting average blood glucose levels over the past few months. This article explores the importance of the eAG test, sharing insights into its normal range and what abnormal readings might mean for you.
How can this knowledge empower you to enhance your diabetes management and reduce health risks? By exploring these key insights, you may find the answers you’ve been looking for. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and together, we can achieve your goals.
eAG Test: Importance in Diabetes Management
Managing blood sugar levels can feel overwhelming, but the estimated Average Glucose (eAG) test is here to help. This essential tool translates A1C results into a format that’s easier to understand, offering an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. By doing so, the eAG test empowers you and your healthcare provider to evaluate how effectively your blood sugar levels are being controlled.
Imagine being able to make timely adjustments to your treatment plan, reducing the risk of complications. Diabetes is the leading cause of death worldwide, so effective management is critical. Studies show that keeping your eAG below 154 mg/dl—equating to an A1C of less than 7%—is vital for minimizing complications. Have you considered how regular exercise can also play a role? For those with type II diabetes, it can lower medication needs by 20%, underscoring the importance of lifestyle changes alongside eAG monitoring.
Dr. Jean Dib, a clinical pharmacist, emphasizes that the introduction of eAG has transformed how patients relate their A1C results to daily blood glucose readings. This connection enhances understanding and encourages proactive management of their condition. It’s important to know that the normal range for the eAG test is between 70 mg/dl and 126 mg/dl. Understanding what constitutes a healthy eAG level in relation to the eAG test normal range is crucial for your journey.
By incorporating eAG monitoring into your care plan, you can take charge of your health. Together, we can achieve your goals, leading to improved health and a better quality of life. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey—we’re here for you, every step of the way.
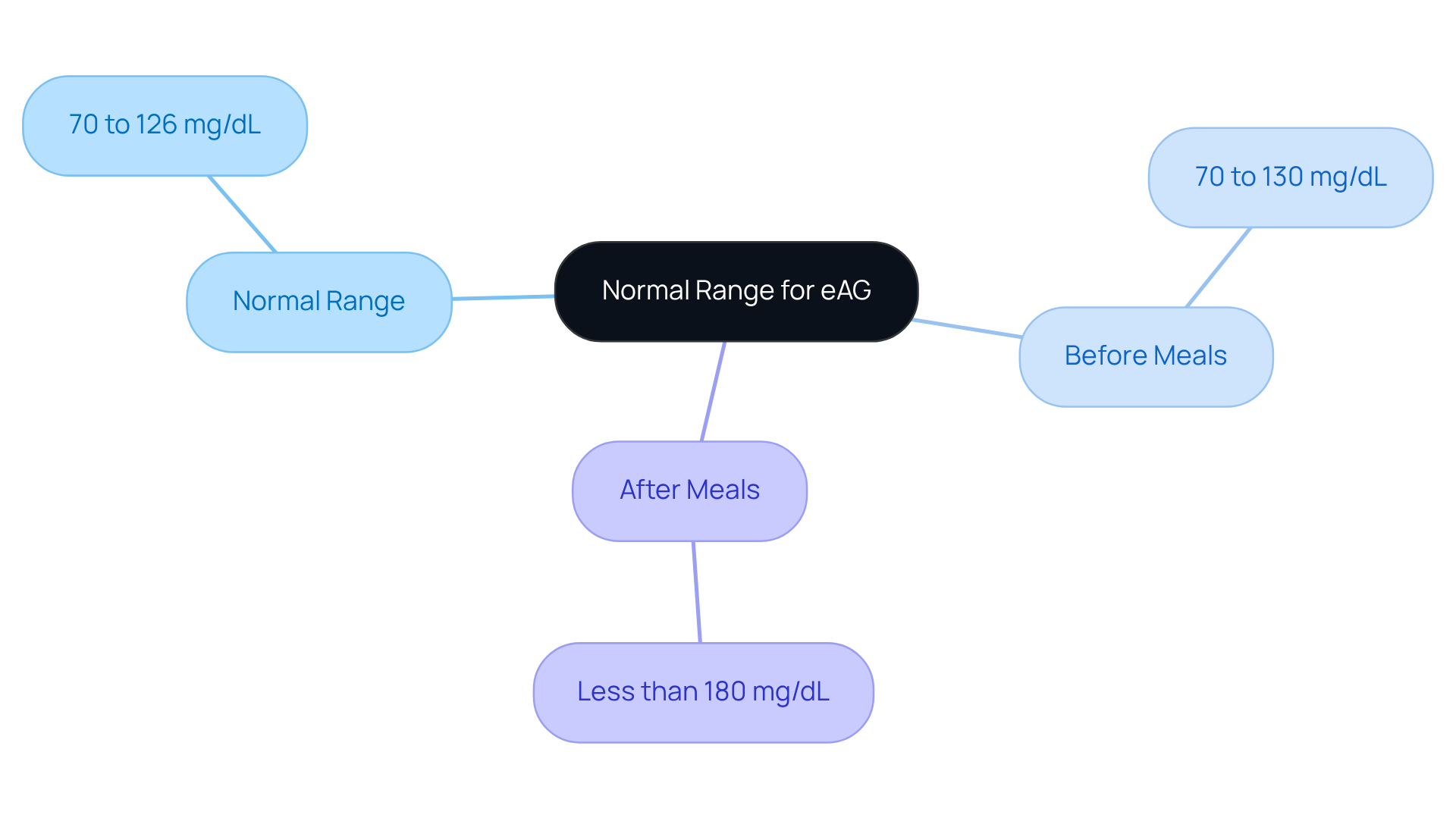
Normal Range for eAG: What You Should Know
Understanding your estimated average sugar (eAG) levels is vital for managing your health. The typical eAG test normal range is generally defined as 70 to 126 mg/dL, with specific benchmarks of 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals. Staying within these limits can significantly reduce the risk of complications related to diabetes. By regularly tracking your eAG readings, you can take important steps toward better health outcomes.
Recent guidelines, including the 2025 Standards of Care from the American Diabetes Association, emphasize the importance of maintaining eAG levels within the eAG test normal range. Research indicates that many individuals successfully manage their eAG within these boundaries, showcasing the effectiveness of personalized care and ongoing support. This approach aligns with the holistic strategies advocated by health professionals, such as those provided by Minimal, which combine medical, nutritional, and fitness expertise.
By understanding and adhering to these eAG guidelines, you can empower yourself in your health journey. However, it’s crucial to note that eAG may not accurately reflect glucose management for individuals with certain conditions, such as kidney disease or sickle cell anemia. Together, we can navigate these challenges and work towards achieving your health goals.
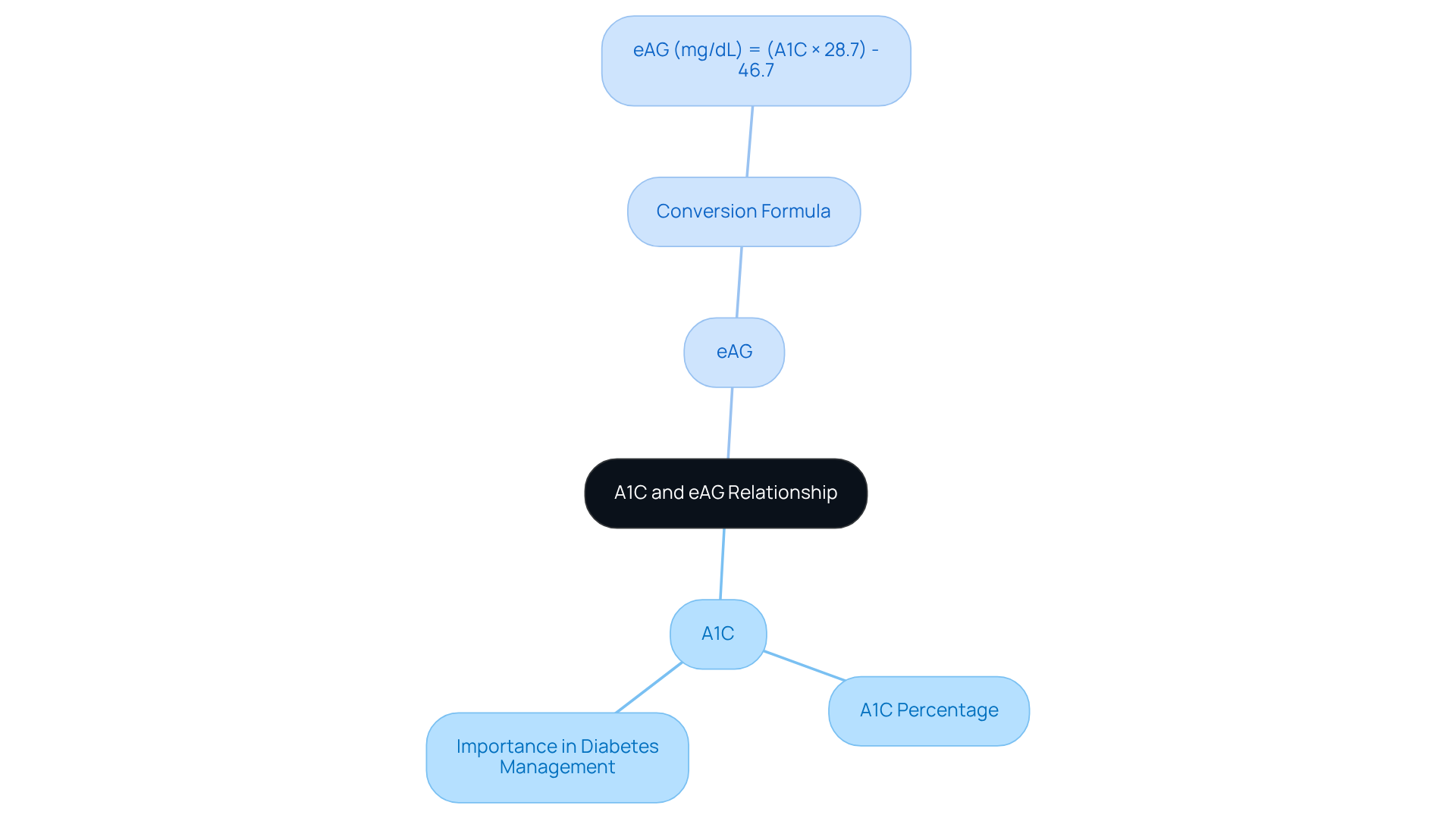
eAG and A1C: Understanding Their Correlation
Understanding your health is crucial, especially when it comes to managing diabetes. The eAG, or estimated Average Glucose, is derived from the A1C test, which measures the percentage of hemoglobin that becomes glycated due to elevated blood glucose levels. This relationship is important because it means that a higher A1C percentage corresponds to a higher eAG.
The formula for converting A1C to eAG is straightforward:
- eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7.
By keeping an eye on both of these metrics, you can gain a clearer picture of your diabetes management.
We understand that navigating these numbers can feel overwhelming, but remember, you are not alone in this journey. By monitoring your A1C and eAG, you empower yourself to take charge of your health. Together, we can achieve your goals and work towards a healthier future.
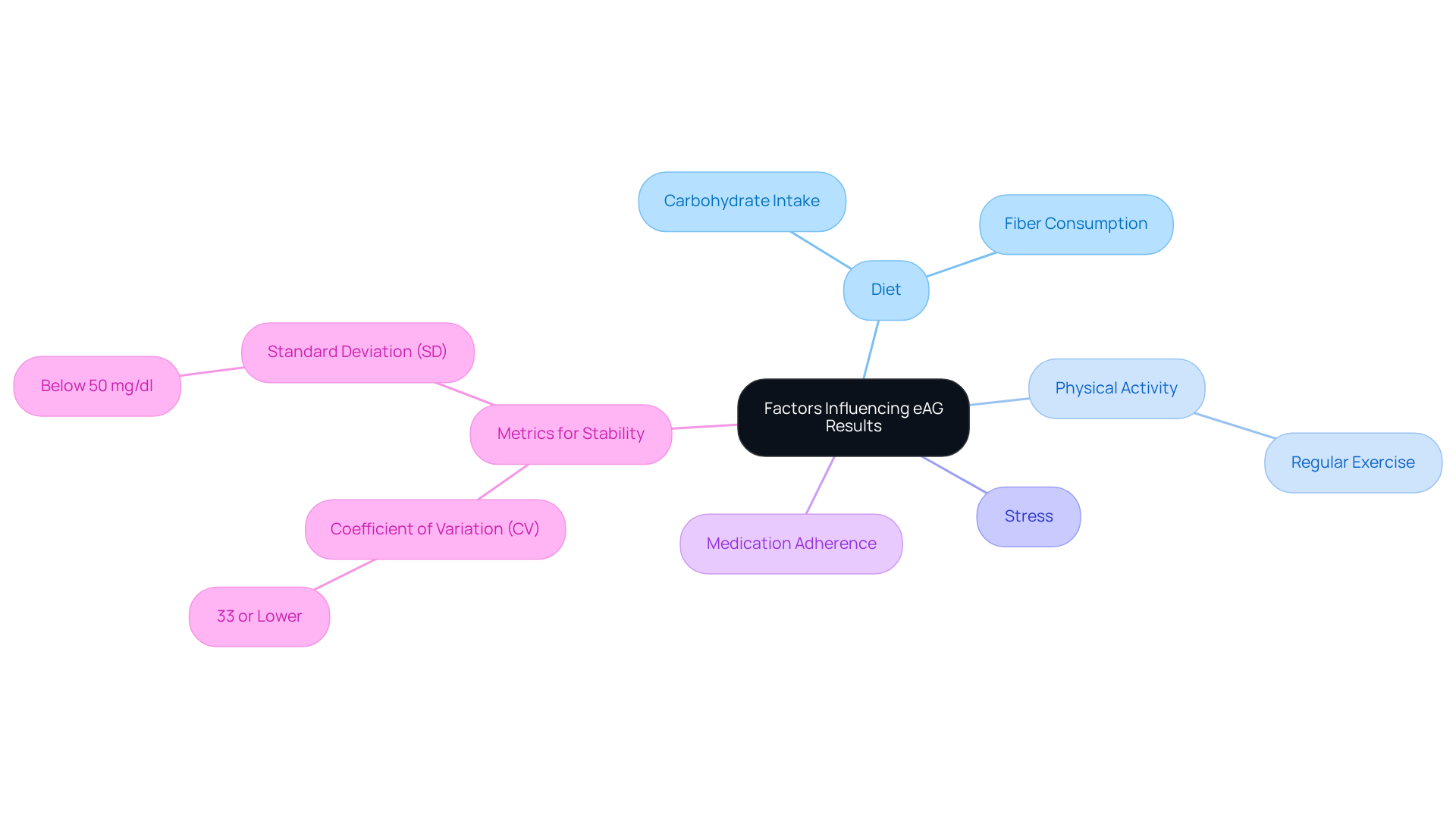
Factors Influencing eAG Results: Key Considerations
Many factors can significantly influence your eAG results, and we understand how overwhelming this can feel. Your diet, physical activity, stress levels, and how well you stick to your medication all play crucial roles. For example, high-carbohydrate meals might lead to noticeable spikes in blood sugar, while regular physical exercise is often linked to lower sugar levels. Conversely, stress can trigger hormonal changes that negatively affect sugar metabolism, leading to increased eAG levels.
Research indicates that maintaining a coefficient of variation (CV) of 33% or lower is vital for stable blood sugar. Typically, individuals with type 2 diabetes show a lower CV compared to those with type 1 diabetes. If your average blood sugar level is around 150 mg/dl, it’s important to aim for a standard deviation (SD) below 50 mg/dl. By grasping these dynamics, you can make informed choices that positively impact your eAG levels and help maintain them within the eAG test normal range.
Consider implementing dietary changes, like reducing carbohydrate intake and boosting fiber consumption, along with regular exercise. These adjustments can lead to meaningful improvements in glucose control. Even small lifestyle changes can yield significant benefits, reinforcing the importance of a comprehensive approach to health management.
It’s also noteworthy that fewer than 7% of individuals engage in self-management education and support (DSMES) services during their first year post-diagnosis. This highlights the critical need for education and assistance in making informed lifestyle choices. As Dr. Chance Miller emphasizes, personalized attention from a dedicated care team can greatly enhance the effectiveness of these lifestyle changes. Remember, together, we can achieve your health goals, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
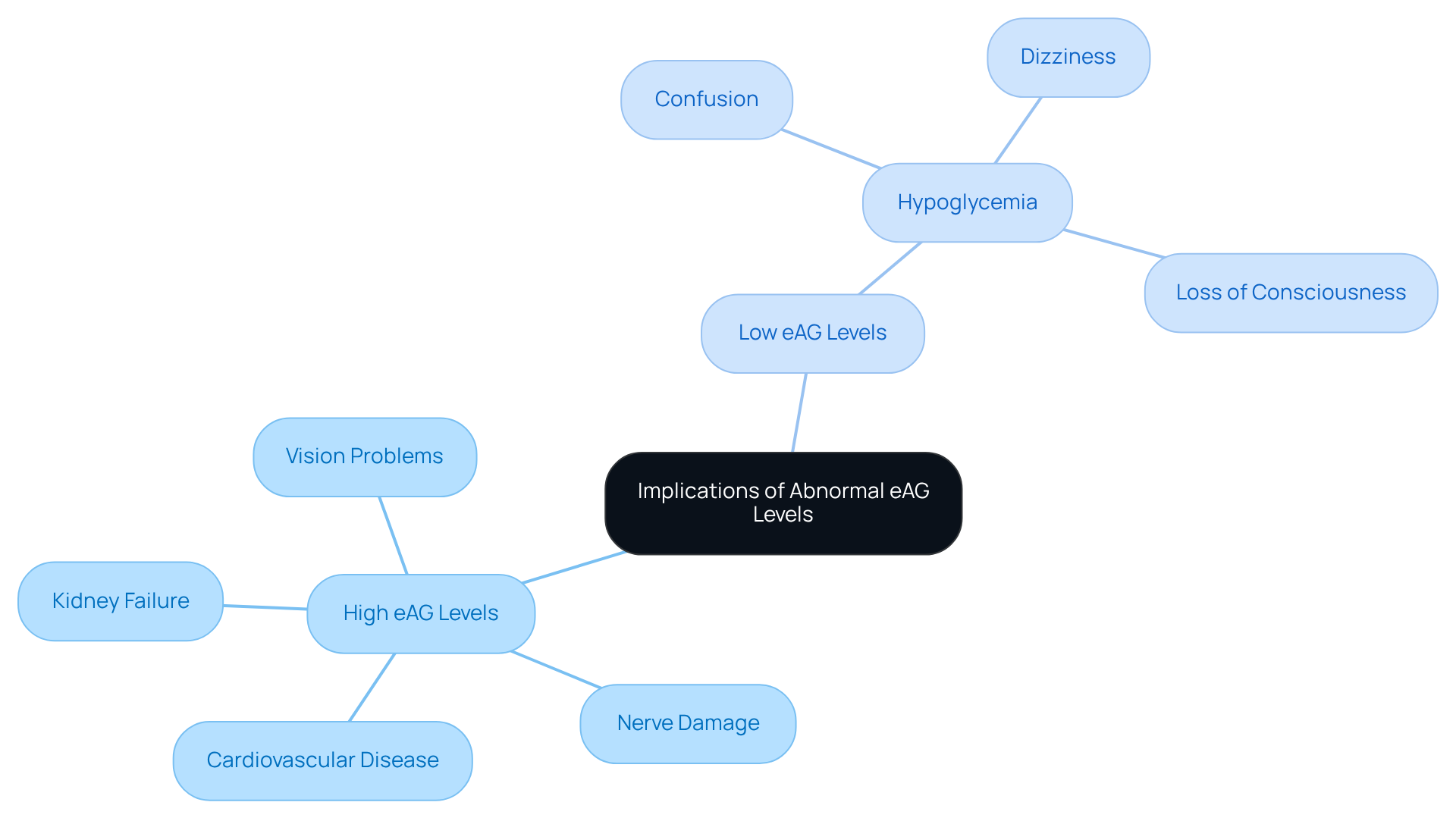
Implications of Abnormal eAG Levels: Health Risks
Unusual estimated Average Glucose (eAG) readings can pose significant health risks, particularly for those grappling with blood sugar issues. When eAG levels rise, it can lead to serious complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage
- Kidney failure
- Vision problems
Have you ever considered how elevated eAG readings might impact your health? Individuals with persistently high eAG levels are at a greater risk of developing cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death among those with blood sugar concerns. In fact, those affected are twice as likely to experience heart disease or stroke compared to those without such conditions. Moreover, elevated eAG values may indicate insufficient blood sugar management, increasing the likelihood of complications.
On the other hand, very low eAG levels can trigger hypoglycemia, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by dangerously low blood sugar levels. Symptoms of hypoglycemia can include:
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
This highlights the importance of immediate intervention.
Real-world examples underscore the consequences of poor eAG control. In 2021, diabetes was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States, a stark reminder of the serious complications associated with elevated eAG. Experts agree that maintaining eAG within the eAG test normal range of below 154 mg/dL, which corresponds to an A1C value of less than 7%, is vital for lowering the risk of complications. Together, we can work towards better health outcomes through routine examinations and personalized care strategies that effectively regulate eAG values. Remember, we’re here for you every step of the way.
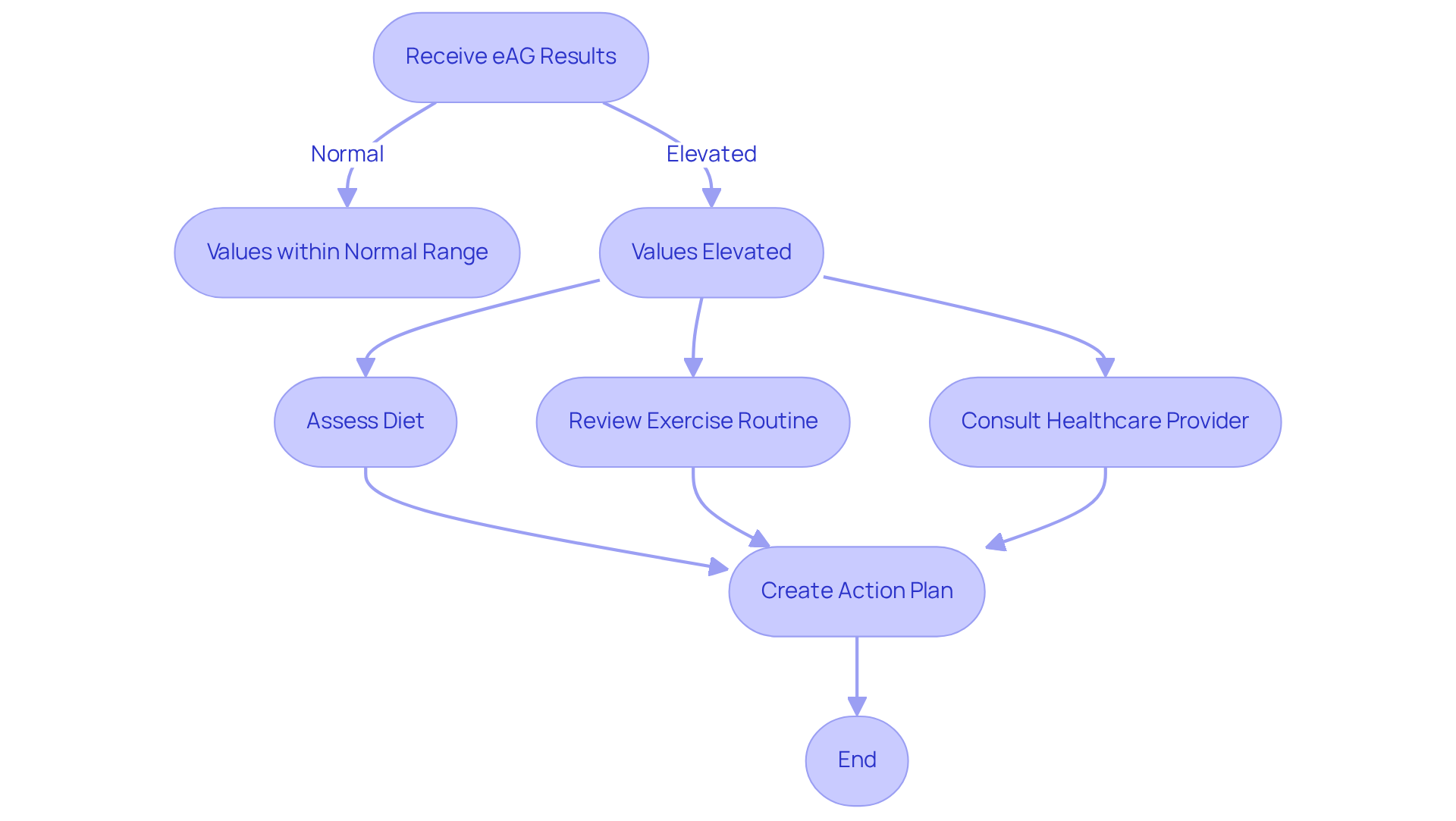
Interpreting eAG Results: A Guide for Patients
Understanding your eAG results is essential to managing your health effectively. Have you ever felt uncertain about where your values fall within the eAG test normal range? Consistently elevated eAG values may signal a need for adjustments in your diet, exercise routine, or medication to achieve the eAG test normal range. Research shows that around 30% of patients might require these adjustments based on their eAG results. This highlights the importance of regular monitoring and proactive management of your health.
Engaging in open conversations with your healthcare provider is vital. Together, you can create a personalized action plan that addresses your unique needs. Keeping a comprehensive record of your eAG readings can help you identify patterns and triggers that influence your blood sugar levels. Remember, as Hans Selye wisely noted, ‘Stress can be described as the rate of wear and tear within the body.’ This underscores the importance of managing stress alongside your sugar concentrations.
By collaborating with healthcare professionals, you can navigate your diabetes management journey more effectively. We’re here for you, and together, we can achieve your health goals. Your proactive steps today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.
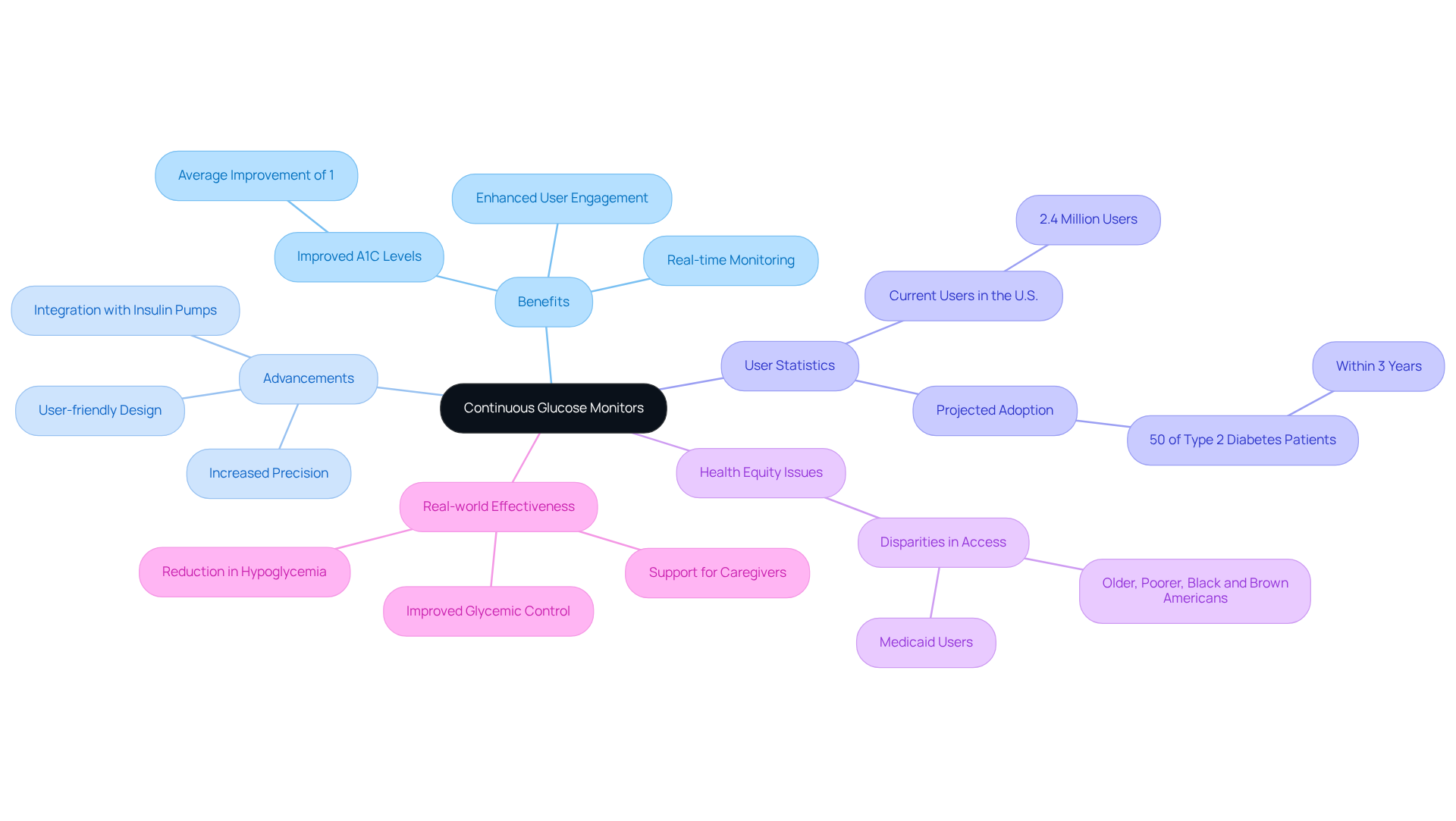
Continuous Glucose Monitors: Enhancing eAG Tracking
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide a dynamic and real-time view of sugar concentrations, significantly enhancing the ability to monitor estimated average sugar levels (eAG). These innovative devices alert users to changes in blood sugar, enabling timely actions that can prevent complications. By using CGMs, individuals gain valuable insights into how their daily choices—like diet and exercise—affect their blood sugar, empowering them to make informed decisions that improve their diabetes management.
Recent advancements in CGM technology have made these devices more precise and user-friendly, allowing for continuous monitoring that surpasses traditional fingerstick methods. Have you ever wondered how your body reacts to different influences, such as food and physical activity? Patients using CGMs can track trends in their glucose readings, which helps them understand these reactions better. This personalized feedback loop not only fosters patient engagement but also leads to better health outcomes. Studies show that CGM users often see significant improvements in their A1C levels, with research indicating an average A1C improvement of about 1 percent.
Currently, around 2.4 million individuals in the U.S. are utilizing CGMs, with projections suggesting that over 50% of Americans with Type 2 conditions will adopt this technology in the next three years. However, disparities in access to CGMs remain, particularly among poorer, older, Black and Brown Americans, and those on Medicaid. This highlights a crucial health equity issue that we must address together.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of CGMs in managing blood sugar. In clinical settings, patients have reported a significant reduction in instances of hypoglycemia and improved overall glycemic control. Continuous glucose monitors not only assist individuals with blood sugar challenges but also support their families, allowing caregivers to monitor glucose levels from a distance during activities like sports. The integration of CGMs into daily routines has transformed care for those facing blood sugar issues, making it clearer and less frustrating for users. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for CGMs to revolutionize diabetes management is promising, offering hope for improved health outcomes for millions. Together, we can navigate this journey towards better health.
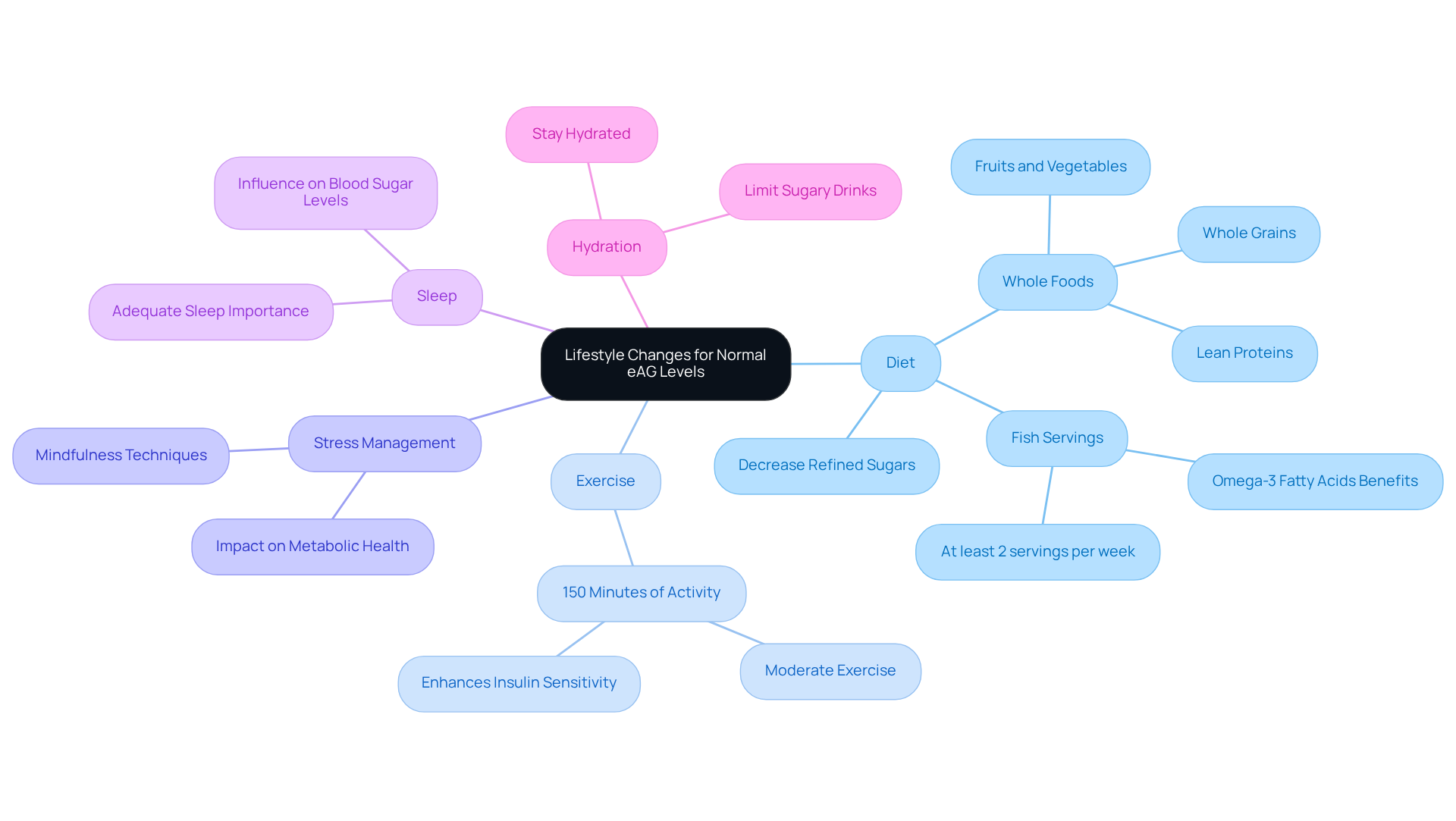
Lifestyle Changes to Maintain Normal eAG Levels
Achieving and sustaining normal eAG values can feel overwhelming, but with strategic lifestyle modifications, it is absolutely within your reach. A balanced diet, rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is essential for your journey. Have you considered how decreasing refined sugars and practicing mindful consumption can stabilize your blood glucose levels? Studies reveal that fewer than 7% of Americans enjoy optimal cardiometabolic health, which underscores the importance of effective lifestyle changes.
Regular physical activity is another key player in this journey. It not only supports weight management but also enhances insulin sensitivity—crucial for effective eAG control. Aim to incorporate at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week; this can lead to significant improvements in your blood sugar management. Additionally, consider including at least two servings of fish each week to benefit from their omega-3 fatty acids.
Managing stress and ensuring adequate sleep are vital components of a holistic approach to diabetes care. Did you know that these factors directly influence your metabolic health? Staying hydrated and being mindful of sugary drinks can also help you maintain stable blood sugar levels. By embracing these practices, you can establish a sustainable lifestyle that promotes the eAG test normal range and enhances overall well-being.
As Pamela Petroski highlights, understanding your personal nutritional requirements is essential. Remember, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all diet for managing blood sugar levels. Together, we can achieve your goals and create a healthier future.
Regular Testing: Essential for eAG Management
Regular testing of estimated Average Glucose (eAG) values is vital for effective diabetes management to ensure they remain within the eAG test normal range. Have you considered how a personalized testing schedule could make a difference in your journey? The American Diabetes Association encourages patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to create a tailored plan that meets their unique needs. This regular oversight not only allows for timely adjustments to treatment strategies but also helps identify concerning patterns in blood sugar levels.
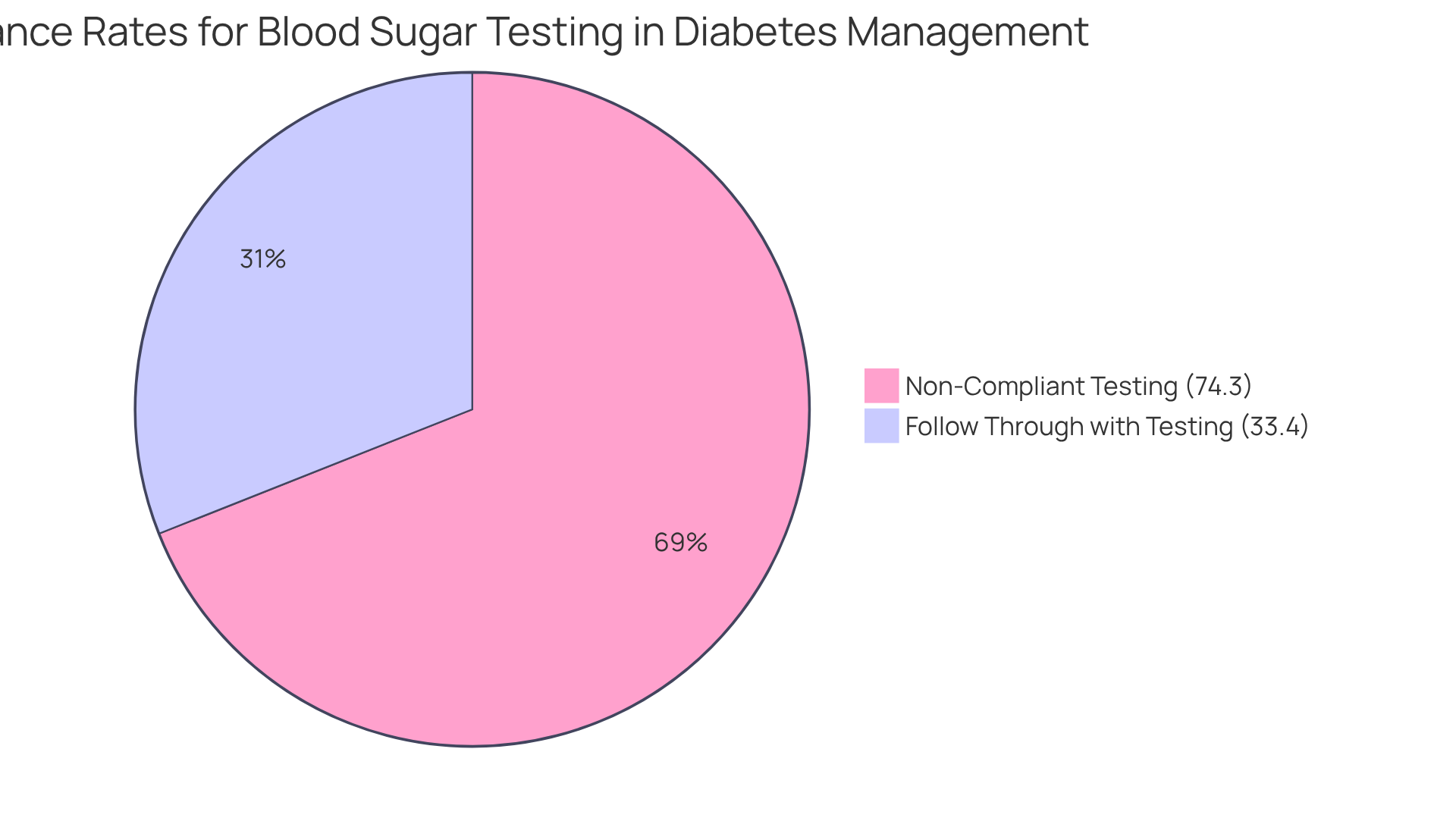
It’s concerning to note that only 33.4% of individuals who meet the criteria for blood sugar testing actually follow through. However, when we include random plasma sugar and unspecified sugar measurements, this number jumps to 74.3%. This highlights a significant gap in regular monitoring among those facing blood sugar challenges. By prioritizing consistent eAG testing to stay within the eAG test normal range, you can take an active role in managing your health, which can lead to improved outcomes.
For instance, individuals who regularly track their eAG levels often maintain their levels within the eAG test normal range, which contributes to better glycemic control. There’s a strong correlation between A1C and average sugar levels, with a notable value of 0.92. This proactive approach empowers you to take charge of your well-being and enhances your overall quality of life. As Grazia Aleppo, MD, wisely states, “Individuals with blood sugar issues should use CGMs—it’s as simple as that.”
Furthermore, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is recommended for older adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who are on insulin therapy. This further underscores the importance of regular monitoring practices. Remember, together, we can achieve your goals for better health.
Minimal: Personalized Solutions for eAG Management
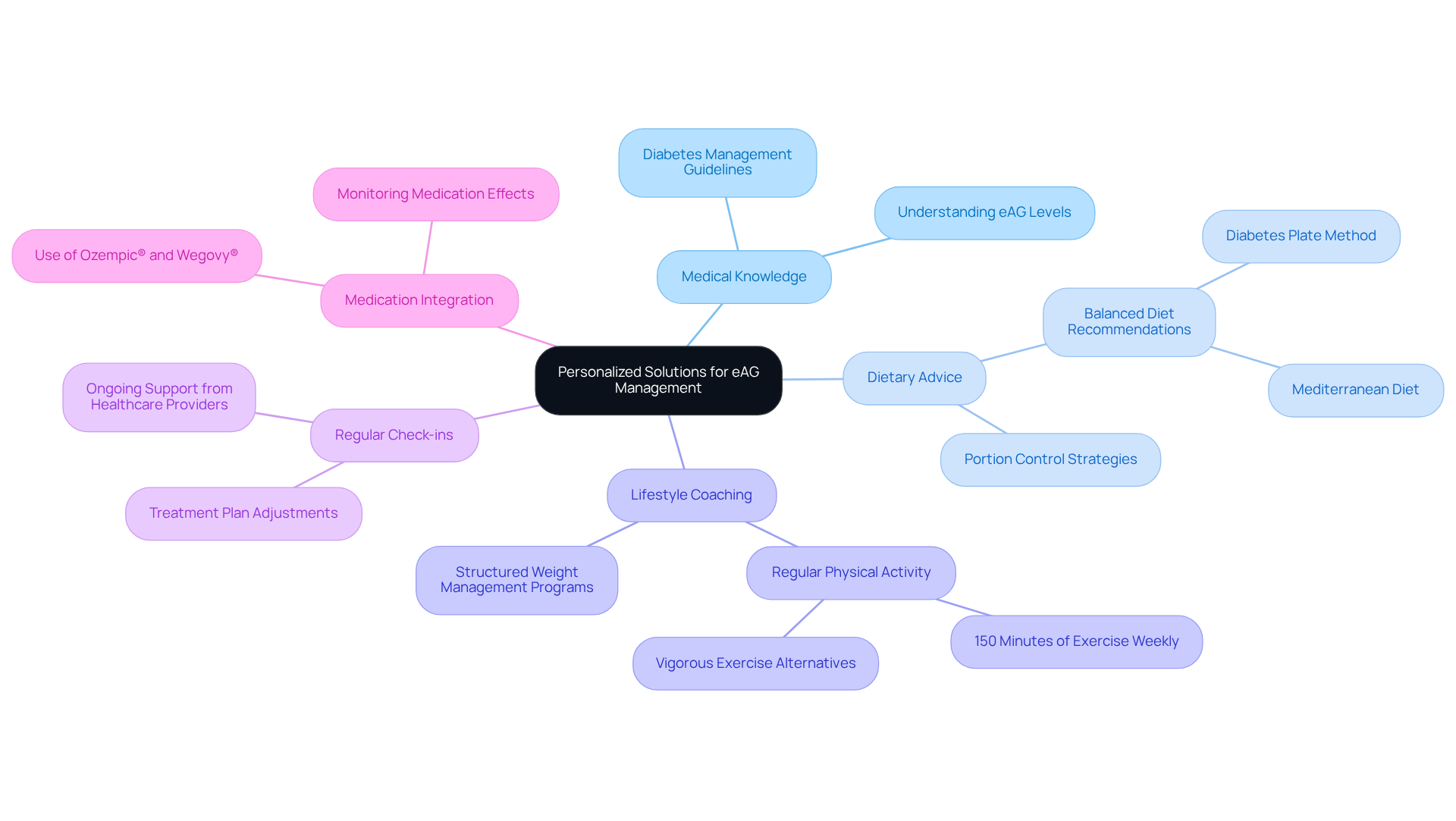
At Minimal, we understand the challenges you face in managing the eAG test normal range, and we’re here to help. Our customized solutions combine medical knowledge, dietary advice, and lifestyle coaching into a comprehensive strategy designed just for you. By tailoring programs to meet your personal needs, we empower you to take charge of your health and effectively manage your condition.
Regular check-ins with your healthcare providers ensure that you receive ongoing support and necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. This consistent care enhances your ability to maintain healthy eAG levels within the eAG test normal range and achieve sustainable health outcomes. In fact, our comprehensive care model has shown remarkable success rates—studies reveal that structured weight management programs can lead to remission in about half of participants, as demonstrated in a clinical trial with 306 individuals living with type 2 diabetes.
Incorporating lifestyle modifications is essential for optimal health management. Embracing a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical exercise can make a significant difference. As Dr. Maria Prelipcean, M.D., wisely notes, “A person can manage their condition by making healthful changes to their diet, exercising frequently, and regularly taking the necessary medications.”
By focusing on these holistic strategies, including the integration of medications like Ozempic® and Wegovy®, we position ourselves as a leader in diabetes care. Together, we can achieve your goals, ensuring that you receive the support you need to thrive. Remember, you are not alone on this journey; we’re here for you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the estimated Average Glucose (eAG) test and its normal range is crucial for effective diabetes management. This test serves as a bridge between complex A1C results and everyday blood sugar values, empowering you to take control of your health. By maintaining eAG levels within the recommended range of 70 to 126 mg/dL, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
This article highlights several key insights into the importance of eAG monitoring:
- It correlates eAG with A1C levels.
- It discusses how lifestyle factors influence eAG results.
- It explains the implications of abnormal eAG levels.
Regular testing and proactive management strategies are essential for achieving optimal health outcomes. Furthermore, advancements in continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology offer innovative solutions that enhance eAG tracking, allowing for more informed decision-making in your daily care.
Ultimately, embracing a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and personalized care can lead to improved diabetes management. By prioritizing eAG testing and understanding its significance, you can take meaningful steps toward a healthier future, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing your overall quality of life. Remember, together, the journey to better health is a collaborative effort, and support is available every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the eAG test and why is it important for diabetes management?
The estimated Average Glucose (eAG) test translates A1C results into an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months, helping individuals and healthcare providers evaluate blood sugar control and make timely treatment adjustments.
What is the target eAG level for minimizing diabetes complications?
To minimize complications, it is vital to keep your eAG below 154 mg/dl, which corresponds to an A1C of less than 7%.
How does regular exercise impact eAG levels for those with type II diabetes?
Regular exercise can lower medication needs by 20% for individuals with type II diabetes, highlighting the importance of lifestyle changes alongside eAG monitoring.
What is the normal range for eAG levels?
The normal range for the eAG test is between 70 mg/dl and 126 mg/dl, with specific benchmarks of 70 to 130 mg/dl before meals and less than 180 mg/dl after meals.
How can tracking eAG readings benefit individuals managing diabetes?
Regularly tracking eAG readings can significantly reduce the risk of complications related to diabetes and empower individuals to take important steps toward better health outcomes.
What is the relationship between eAG and A1C?
The eAG is derived from the A1C test; a higher A1C percentage corresponds to a higher eAG. The formula to convert A1C to eAG is eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7.
Are there any conditions that may affect the accuracy of eAG readings?
Yes, eAG may not accurately reflect glucose management for individuals with certain conditions, such as kidney disease or sickle cell anemia.