Overview
If you’re looking to decrease your A1C levels and embark on a weight loss journey, it’s important to focus on:
- A balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Effective stress management
- Good sleep hygiene
We understand that this can feel overwhelming, but there are critical strategies that can help you along the way. Incorporating whole foods into your meals, engaging in physical activity that you enjoy, and maintaining good sleep hygiene are all essential steps. Together, these practices work to improve glucose regulation and enhance your overall health, making weight management more achievable.
Have you considered how these changes could positively impact your life? By nurturing your body with wholesome foods and staying active, you are taking significant strides toward better health. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Many have found success by embracing these habits, and we believe you can too. Let’s take it one step at a time, focusing on small, manageable changes that lead to lasting results.
As you navigate this path, keep in mind that every effort counts. Celebrate your progress, no matter how small, and stay committed to your goals. Together, we can achieve the healthy lifestyle you desire. You’re capable of making these changes, and with support and dedication, a brighter, healthier future is within reach.
Introduction
Understanding the significance of A1C levels is crucial for anyone on a weight loss journey. These measurements can reveal much about your overall health and your risk for diabetes. By exploring effective strategies to decrease A1C, you can unlock the potential for better health outcomes, improved energy levels, and enhanced weight management.
However, the path to achieving optimal A1C levels can often feel daunting. What are the most effective steps you can take to navigate dietary changes, exercise routines, and stress management?
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; together, we can achieve your goals and foster a healthier future.
Understand A1C: Importance and Measurement
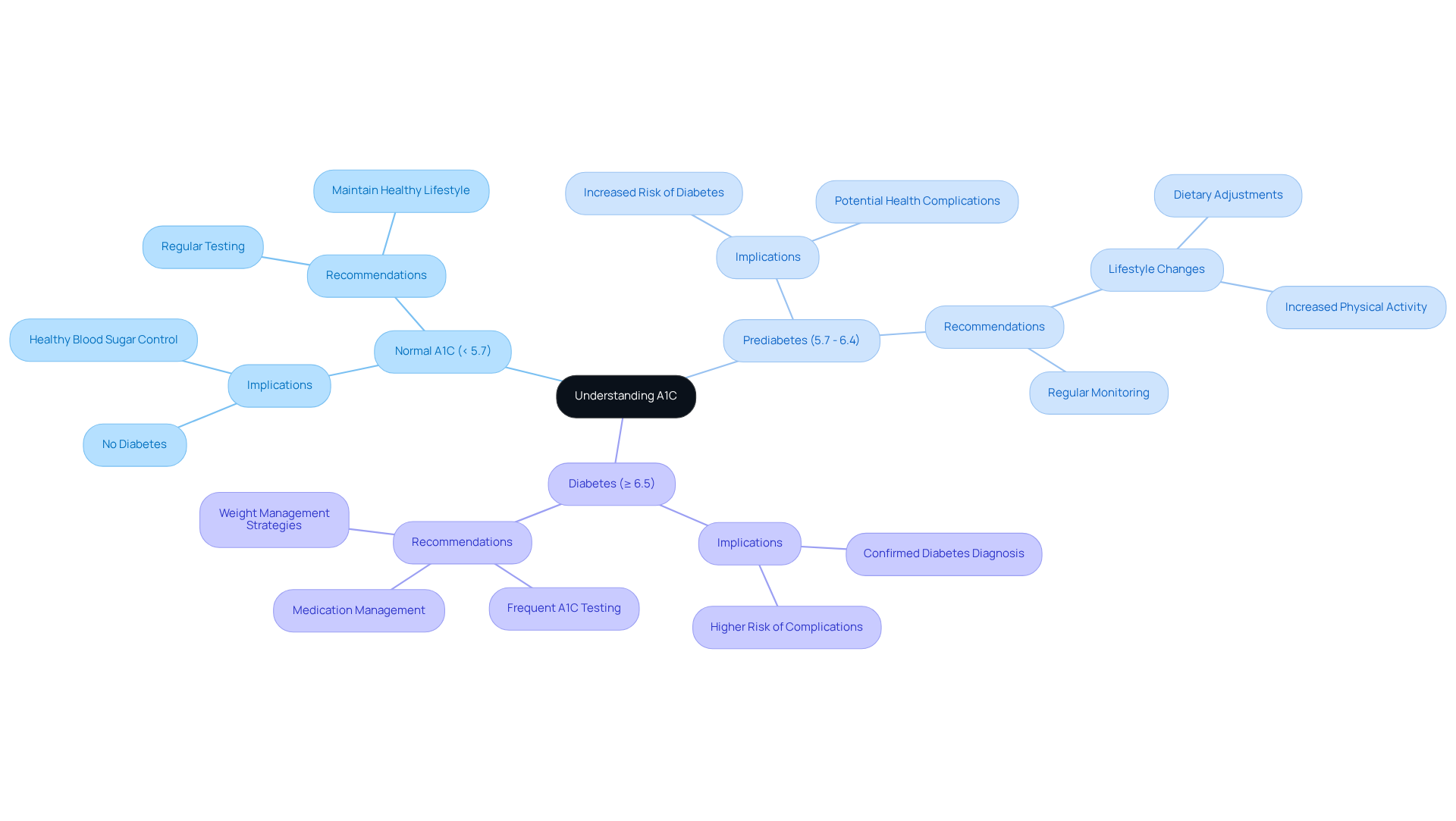
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is a vital test that measures your average glucose levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. Understanding your A1C measurement is crucial. A normal A1C reading is below 5.7%, while values between 5.7% and 6.4% signal prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes. This knowledge not only assesses your risk for diabetes but also reveals how well your sugar is being controlled.
To measure A1C, a healthcare provider will take a sample, which can be done without fasting, making it convenient for regular monitoring. It’s recommended that individuals with diabetes have this test at least twice a year, or more often if there are changes in treatment. Regular A1C monitoring is essential for guiding dietary and lifestyle changes, as it helps you understand how to decrease A1C, serving as a crucial first step in your weight loss journey.
Have you ever wondered how A1C monitoring can impact your weight loss? Real-world examples show that individuals who actively manage their A1C numbers often learn how to decrease A1C and experience better weight management results. Keeping an A1C below 6.5% can help prevent long-term complications related to diabetes, such as nerve damage and kidney disease.
Healthcare professionals stress the importance of A1C testing in managing diabetes. Consistent monitoring allows for timely adjustments to treatment strategies, ensuring that you can effectively control your blood sugar. As experts note, “A well-controlled A1C helps reduce your risk of damage to your eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart.”
In summary, understanding how to decrease A1C values and accurately assessing them is essential for effective diabetes management and weight loss. By prioritizing A1C testing, you can take proactive steps toward better health and an improved quality of life. Remember, together, we can achieve your goals.
Plan Your Diet: Foods to Include and Avoid
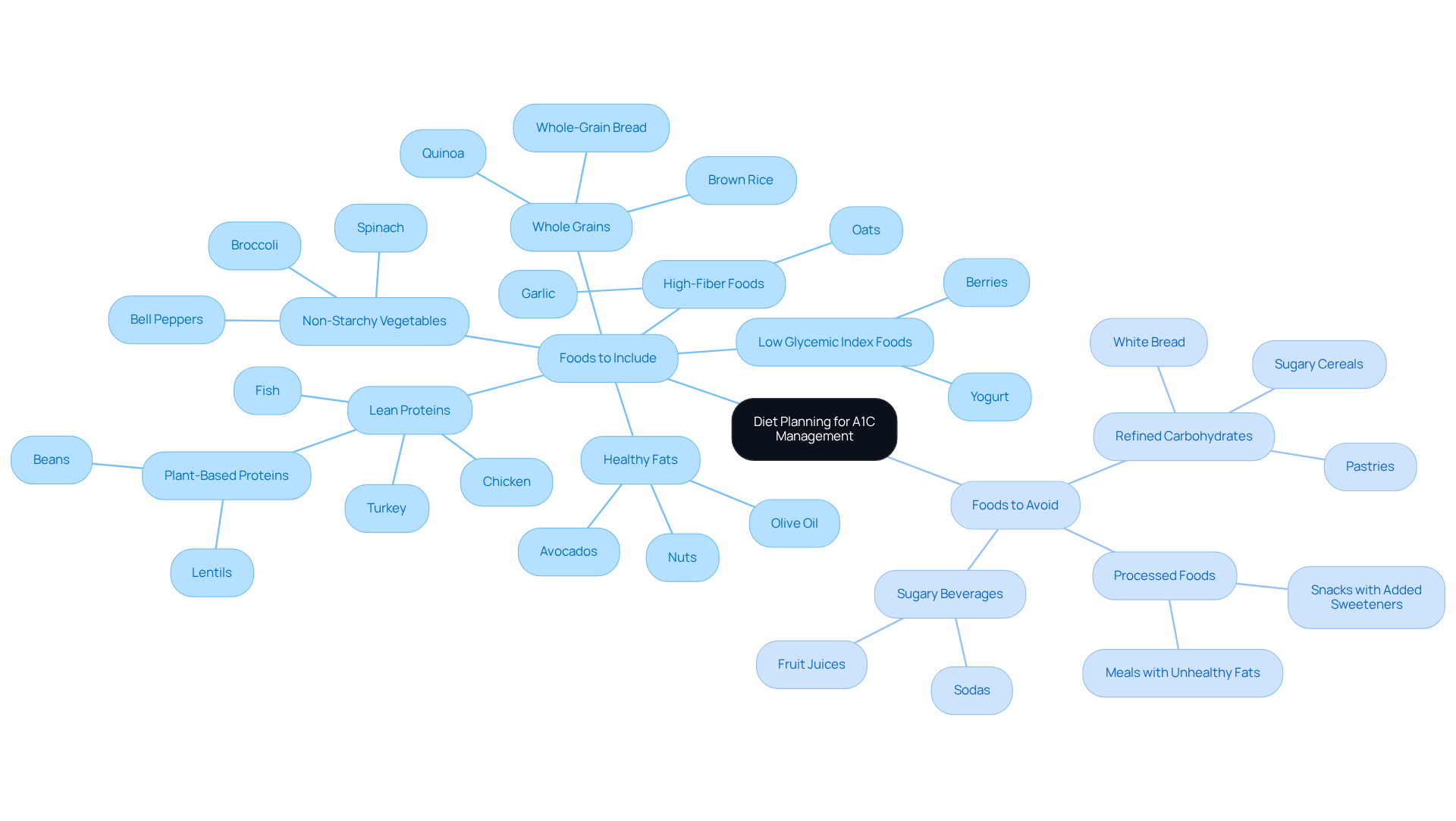
To effectively understand how to decrease A1C values, it’s important to prioritize a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. We understand that navigating dietary changes can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to support you. Here are some essential guidelines that can help you on this journey:
Foods to Include:
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Consider incorporating broccoli, spinach, and bell peppers into your meals. These vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, which aids digestion and helps with blood sugar control.
- Whole Grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, and whole-grain bread. Research shows that whole grains can stabilize glucose levels and are linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Lean Proteins: Including sources like chicken, turkey, fish, and plant-based proteins such as beans and lentils can support muscle health and keep you feeling full.
- Healthy Fats: Foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil are not only delicious but also contribute to heart health and assist in weight management, making them beneficial for your overall well-being.
- High-Fiber Foods: Aim for 25-30 grams of fiber each day. Fiber plays a crucial role in regulating glucose concentrations and enhancing digestive wellness. Foods such as oats and garlic can also help in managing glucose levels.
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Including items with a low glycemic index may assist you in managing your glucose concentrations effectively.
Foods to Avoid:
- Refined Carbohydrates: It’s wise to limit your intake of white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals. These can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels and increase the risk of hyperglycemia.
- Sugary Beverages: Steering clear of sodas and fruit juices that are high in sweetness can greatly improve your glucose regulation.
- Processed Foods: Avoid snacks and meals that contain high levels of added sweeteners and unhealthy fats, as they can hinder your dietary efforts.
Meal Planning Tips:
- Use the Plate Method: A simple way to create balanced meals is to fill half your plate with vegetables, a quarter with lean protein, and a quarter with whole grains. This method can help you visualize your portions better.
- Prepare Meals at Home: Cooking at home gives you control over your ingredients and portion sizes, making it easier to stick to your dietary guidelines.
- Consistent Monitoring: Regularly checking your glucose values can empower you to understand how to decrease A1C effectively and make necessary adjustments to your diet.
Remember, together we can achieve your goals, and every small step counts in this journey towards better health.
Incorporate Exercise: Effective Workouts for A1C Reduction
Consistent physical activity is crucial for understanding how to decrease A1C values and improving overall health. Have you considered how incorporating exercise into your routine can positively impact your well-being? Here are some effective workouts to consider:
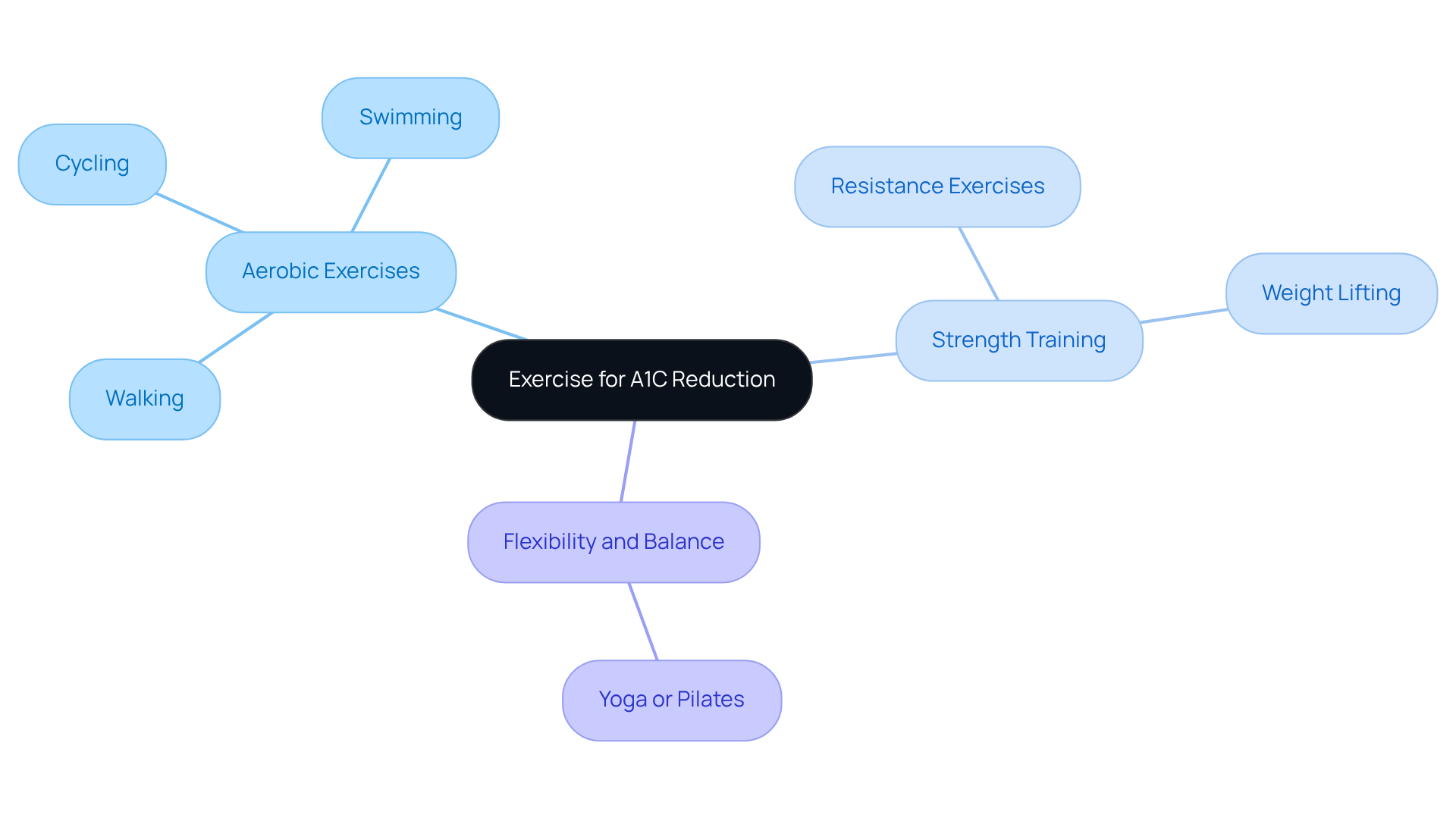
Aerobic Exercises:
- Walking: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity walking each week, ideally broken down into 30-minute sessions five times a week. This straightforward activity can greatly influence blood glucose amounts and general fitness. Research indicates how to decrease A1C values significantly by walking for 30 minutes five days a week.
- Cycling: Whether on a stationary bike or cycling outdoors, this exercise enhances cardiovascular health and can be easily modified to suit your individual fitness capabilities. It’s a great way to stay active and enjoy the outdoors!
- Swimming: A low-impact choice that offers a comprehensive workout while being easy on the joints, making it appropriate for individuals of all fitness abilities. Have you thought about how refreshing a swim can be?
Strength Training:
- Resistance Exercises: Incorporate bodyweight exercises such as squats, lunges, and push-ups at least twice a week. These exercises help build muscle mass, which improves insulin sensitivity and aids in weight management, providing insight on how to decrease A1C. Remember, every little bit helps!
- Weight Lifting: Participating in weight training can boost muscle mass, resulting in higher calorie expenditure even at rest, which is advantageous for regulating glucose amounts. It’s empowering to see your strength grow!
Flexibility and Balance:
- Yoga or Pilates: These practices not only improve flexibility but also reduce stress and enhance overall well-being, contributing positively to blood glucose management. It is recommended to perform flexibility and balance exercises at least 2-3 times per week, especially for older adults. How wonderful would it be to feel more relaxed and centered?
Tips for Success:
- Discover activities you enjoy to maintain motivation and consistency. What makes you feel good?
- Consider joining a group or class for social support, which can enhance adherence to exercise routines. Together, we can achieve your goals!
- Track your workouts to monitor progress and stay accountable, helping you stay focused on your health goals. As King observes, exercise aids your body in becoming more responsive to insulin and is an effective method for learning how to decrease A1C by reducing blood glucose amounts during and for up to 24 hours following exercise. Let’s take this journey together!
Manage Stress and Sleep: Strategies for Better Health
Managing stress and ensuring quality sleep are vital factors in understanding how to decrease A1C readings. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed, but there are strategies that can help you navigate this journey with confidence.
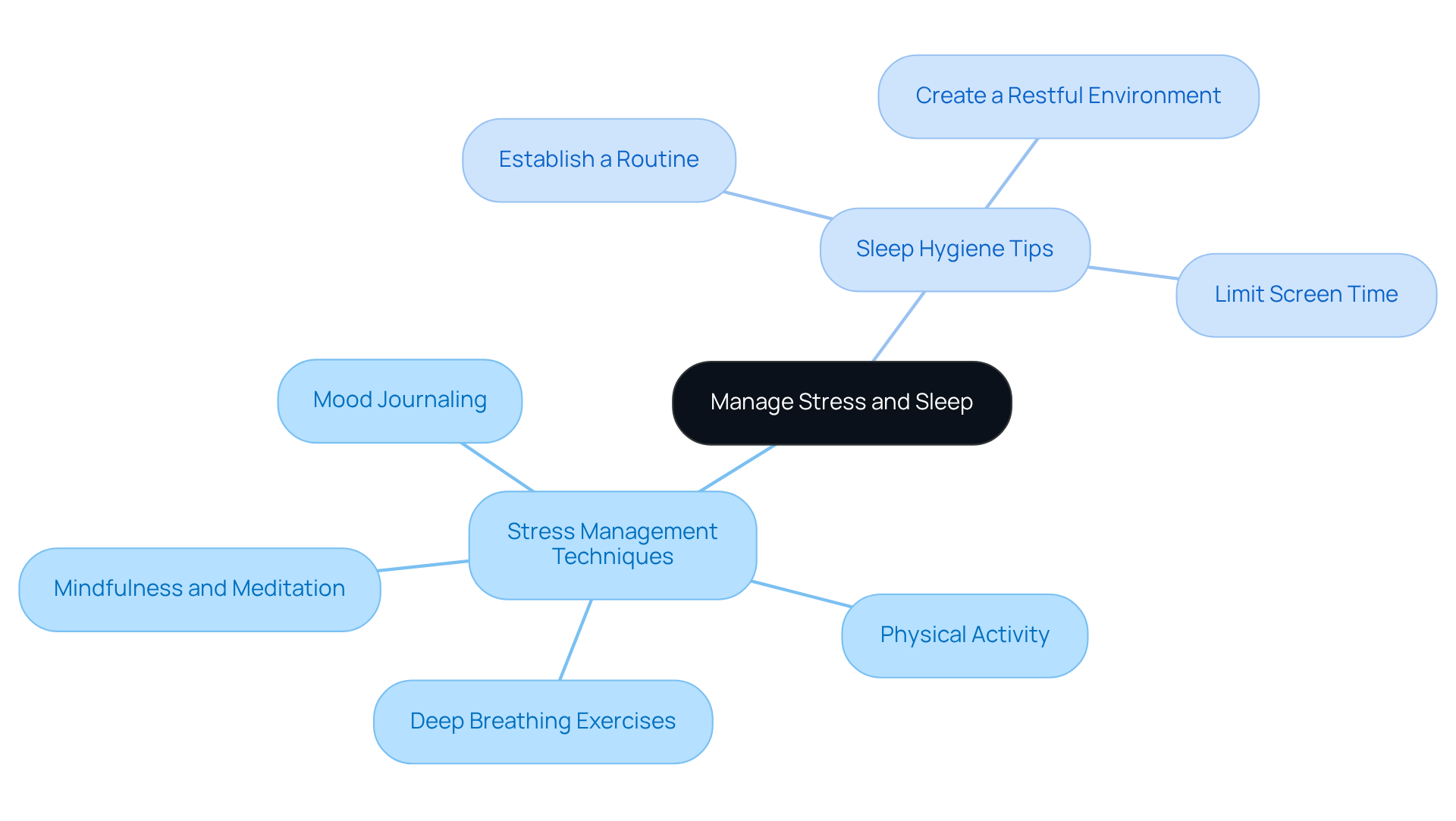
Stress Management Techniques:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Have you considered practicing mindfulness or meditation for at least 10 minutes daily? This simple act can significantly reduce stress and improve your focus. Remember, chronic stress can lead to increased insulin resistance, complicating diabetes management, so finding effective coping strategies is crucial.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is a wonderful way to alleviate stress and boost your mood. Engaging in physical activity, even for brief periods, can greatly decrease stress and enhance your overall well-being.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Incorporating deep breathing techniques can help calm your nervous system. Try breathing in for a count of four and exhaling for a count of six—this can be particularly effective in stressful situations.
- Mood Journaling: Keeping a mood journal to reflect on your emotions and experiences can be incredibly beneficial. This practice not only helps you manage stress but also promotes mental well-being by providing insights into your feelings.
Sleep Hygiene Tips:
- Establish a Routine: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can help regulate your body’s internal clock. Stability in sleep patterns is essential for sustaining circadian rhythms, which play a crucial role in regulating glucose levels.
- Create a Restful Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to promote better sleep quality. A conducive sleep environment can help mitigate issues like obstructive sleep apnea, which is common among individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Limit Screen Time: Reducing exposure to screens at least an hour before bedtime can improve sleep onset. This practice helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle and enhances overall sleep quality.
Importance of Sleep:
Research shows that poor sleep can lead to increased insulin resistance and higher blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your health goals. Prioritizing sleep not only aids in blood sugar regulation but also teaches how to decrease A1C, enhancing overall health outcomes and making it a crucial component of effective diabetes management. As Anna Vidovszky notes, connection with others can also be a powerful way to combat stress, so consider reaching out to friends or loved ones for support. Together, we can achieve your goals and foster a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion
Understanding how to effectively decrease A1C levels is vital for individuals seeking weight loss and improved overall health. By monitoring A1C values, you can gain insights into your blood sugar control and make informed decisions about your dietary and lifestyle choices. This proactive approach not only aids in weight management but also significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
Key strategies to consider include:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods
- Incorporating regular exercise
- Managing stress and sleep
Foods such as non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins play a crucial role in stabilizing glucose levels. Physical activities like walking and strength training enhance insulin sensitivity. Additionally, prioritizing mental well-being through mindfulness and ensuring adequate sleep are essential components of effective A1C management.
Ultimately, the journey to lower A1C levels is multifaceted and requires commitment and a holistic approach. By implementing these strategies, you can not only achieve your weight loss goals but also enhance your quality of life. Embracing these changes is not just about numbers; it’s about fostering a healthier lifestyle that empowers you to take control of your health and well-being. Remember, together, we can achieve your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is a test that measures your average glucose levels over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. It is important because it helps assess your risk for diabetes and reveals how well your blood sugar is being controlled.
What do different A1C readings indicate?
A normal A1C reading is below 5.7%. Values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes.
How is A1C measured?
A1C is measured through a blood sample taken by a healthcare provider, which can be done without fasting, making it convenient for regular monitoring.
How often should individuals with diabetes have their A1C tested?
It is recommended that individuals with diabetes have their A1C tested at least twice a year, or more frequently if there are changes in treatment.
How does A1C monitoring relate to weight loss?
Regular A1C monitoring helps individuals understand how to decrease their A1C levels, which can lead to better weight management results. Keeping an A1C below 6.5% can help prevent long-term complications related to diabetes.
What are the long-term complications of poorly managed A1C levels?
Poorly managed A1C levels can lead to long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and damage to the eyes and heart.
Why is consistent A1C monitoring important for diabetes management?
Consistent A1C monitoring allows for timely adjustments to treatment strategies, ensuring effective control of blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications.